Most UK businesses file their VAT return on time. But meeting the deadline and getting the return right are two different things. When preparation starts too late, errors slip through, incorrect VAT treatment, missing invoices, unreconciled accounts and these issues often don’t surface until HMRC raises a query or a penalty notice arrives.
The difference between a smooth VAT process and a stressful one comes down to preparation. Not the work done in the final few days before the deadline, but the steps taken throughout the quarter to keep records accurate and complete.
This guide explains the difference between VAT deadlines and VAT preparation, where businesses typically go wrong and how to fix the process with better bookkeeping, checks and support.
This guide covers:
- The difference between VAT deadlines and VAT preparation
- Key HMRC VAT deadlines and VAT return deadlines
- Common VAT filing mistakes and VAT bookkeeping errors
- How to reduce errors in VAT return preparation
- Best practices and VAT return services that help businesses stay compliant
Understanding the Real Difference Between VAT Deadlines and VAT Preparation
Before improving anything, businesses need to separate these two ideas clearly:
VAT Deadlines
These are the dates by which VAT returns and payments must reach HMRC.
If a VAT return is submitted late, HMRC applies a points-based system and a financial penalty can apply once a threshold is reached.
VAT Preparation
This is the work required before the deadline:
- collecting invoices and receipts
- checking VAT treatment
- reconciling sales and purchases
- reviewing VAT return boxes
- validating numbers before submission
The problem: businesses focus on VAT deadlines, but ignore VAT preparation timelines.
HMRC VAT Deadlines: What You Need to Know and When?
Most UK VAT registered businesses file returns quarterly. Here are the official deadlines and how they apply to most UK businesses.
Quarterly VAT Returns: Filing and Payment Rule
VAT returns are usually due 1 month and 7 days after the end of the VAT period (unless using annual accounting or special arrangements). This is commonly explained across VAT deadlines guidance articles.
Example: If your VAT quarter ends 31 March, the deadline is usually 7 May.
Quarterly Deadlines
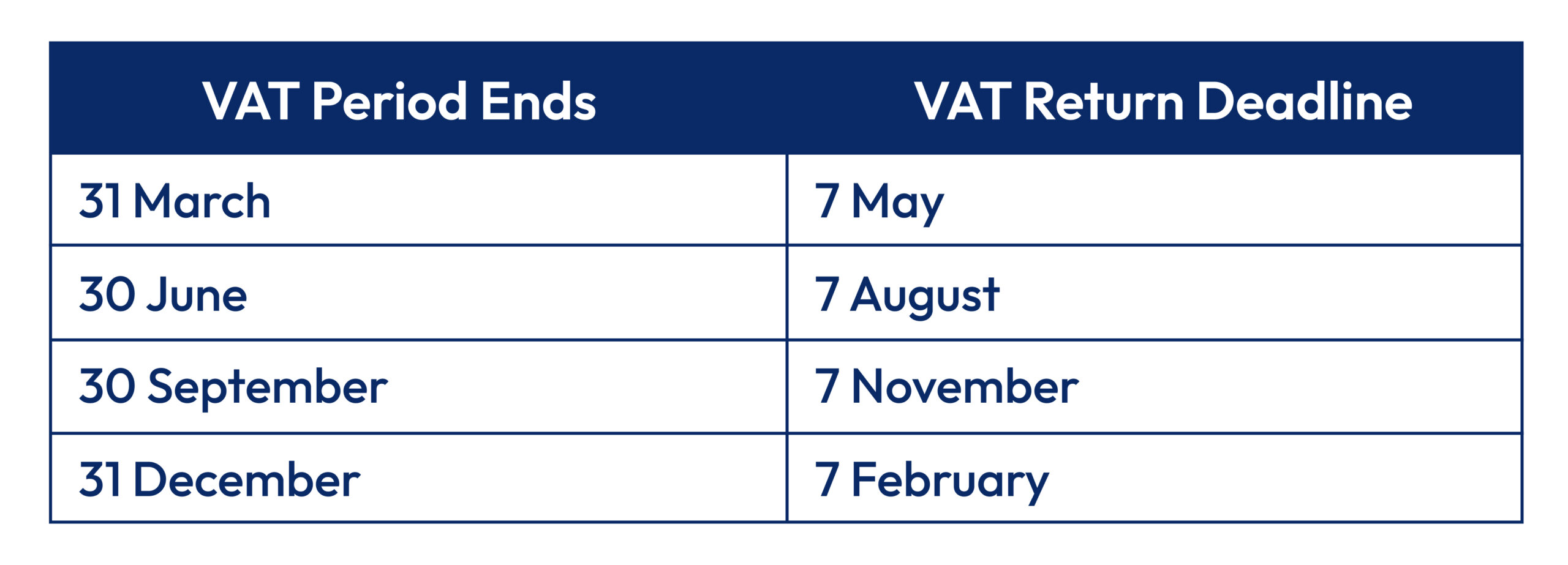
This is why VAT preparation needs to start weeks earlier, not days earlier.
Why Businesses Miss VAT Deadlines?
Most businesses do not miss VAT return deadlines because they forget the date.
They miss it because:
- paperwork is missing
- transactions are not posted
- VAT coding is inconsistent
- bank and VAT accounts are not reconciled
- the business waits for the accountant to “sort everything”
This is consistent with the common themes in VAT mistakes and penalty guidance articles.
Where VAT Return Preparation Fails?
This is where the gap between VAT deadlines and VAT preparation shows up.
1. Unreconciled Records
If the bank is not reconciled, VAT figures are unreliable. It becomes impossible to confirm whether all sales and purchases are captured.
This leads to VAT bookkeeping errors and wrong VAT box totals.
2. Wrong VAT Treatment
This includes:
- reclaiming VAT where it is not allowed
- applying the wrong VAT rate
- treating items incorrectly (especially entertainment and vehicles)
These are common VAT mistakes noted in VAT mistakes guidance.
3. Missing Purchase Invoices
Late supplier invoices create underclaimed VAT. Businesses then want to “adjust later”, which creates extra admin and correction risk.
4. Manual Processes with No Checks
Manual spreadsheets, late document uploads and inconsistent coding create errors that are only visible at filing stage.
5. Late Approvals
In many businesses, VAT return preparation is completed, but approval is delayed. That is a risky pattern. Approval should be part of the timetable.
VAT Return Penalties: What Happens If You File Late?
Businesses need a clear, factual view of what is at stake.
Late Submission Penalties
HMRC applies penalty points when VAT returns are late. Once you reach the points threshold, a financial penalty can apply.
Late Payment Penalties
Separate penalties can apply if VAT is paid late. Many articles highlight the 15-day and 30-day windows that trigger percentage-based penalties.
The key issue is that businesses confuse “submitted” with “paid”. Both matter.
VAT Timeline (Typical Small Business)
| Week | What often happens? |
|---|---|
| Week 1 after VAT period ends | No action taken |
| Week 2 | Missing invoices noticed |
| Week 3 | Bookkeeping catch-up begins |
| Week 4 | Accountant receives incomplete data |
| Last 3 to 5 days | Rushed VAT return preparation |
| Deadline day | Filing rushed or missed |
This is why “VAT deadlines management” is not enough. Preparation must be scheduled.
What Good VAT Preparation Looks Like?
A good accounts team does not “prepare VAT returns”.
They run a repeatable VAT preparation process.
| Step | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Complete bookkeeping entries | All sales and purchases recorded |
| Reconcile bank | No missing transactions |
| Review VAT coding | VAT rates and treatments corrected |
| Check VAT control account | VAT position validated |
| Run draft return | VAT return preparation begins |
| Internal review | Errors spotted before submission |
| Approval and filing | Return submitted and payment scheduled |
This structure reduces VAT filing mistakes.
Common VAT Mistakes That Lead to Penalties
Based on VAT mistakes content from UK accounting firms and VAT guidance discussions, the most common VAT mistakes include:
- reclaiming VAT where it should not be reclaimed
- missing sales invoices
- inconsistent VAT codes
- incorrect partial exemption handling
- not keeping clear digital records (MTD-related)
Even a small mistake can create time-consuming corrections later.
Best Practices to Stay VAT Compliant with HMRC
These actions keep the VAT process stable and reduce risk.
1. Start VAT Preparation Early
A strong rule: start VAT preparation by Day 10 after quarter end.
2. Keep Bookkeeping Consistent
Bookkeeping and VAT compliance are linked. If bookkeeping slips, VAT becomes reactive.
3. Use a Standard Review Checklist
Businesses should use the same review checklist every quarter.
4. Keep Documentation Organised
Digital document collection supports better VAT return preparation and reduces missing invoice issues.
5. Use Accountant Support Properly
Accountants help most when:
- the records are ready
- coding is consistent
- questions are raised early
- the review is structured
When to Use VAT Return Services?
Some businesses are not set up to manage VAT internally.
This is where VAT return services can help, especially for:
- growing businesses with high transaction volume
- businesses with mixed VAT rates
- directors who want compliance certainty
- teams with limited internal finance capacity
VAT return services typically cover:
- VAT return preparation
- VAT reconciliation
- review of VAT bookkeeping errors
- submission under MTD-compatible software
If VAT preparation is becoming last-minute every quarter, it may be time to move to structured VAT return services. This reduces errors, improves compliance control and saves internal time.
How Accountants Help Businesses Avoid VAT Mistakes?
Accountants help most when the business gives them clean inputs.
Here is the correct division of responsibility:
| Business’s Role | Accountant’s Role |
|---|---|
| Maintain clean records | Review VAT logic and compliance |
| Upload documents on time | Confirm VAT treatment and risk |
| Approve on schedule | Submit and advise on corrections |
Conclusion
VAT deadlines are fixed. VAT preparation is not. That is where businesses go wrong.
Most VAT return penalties and VAT filing mistakes are not caused by deadline pressure alone. They come from late bookkeeping, missing documents, unreconciled accounts and weak review processes. A reliable VAT preparation routine, supported by clear checks and timely reporting, is the practical way to stay VAT compliant with HMRC.
For businesses that struggle every quarter, structured VAT return services and accountant support can reduce errors, improve accuracy and make VAT compliance consistent rather than reactive.
FAQs
When are VAT returns due in the UK?
Most VAT returns are due one month and seven days after the VAT period ends, often as quarterly VAT returns.
What are VAT late filing penalties?
HMRC uses penalty points for late submissions and applies financial penalties once a points threshold is reached.
How long do businesses have to prepare VAT returns?
Technically until the deadline, but good VAT return preparation should begin within 10 days after the VAT period ends.
Can accountants submit VAT returns for clients?
Yes, accountants can submit VAT returns for clients under MTD-compatible software and agreed authorisation.
How to stay VAT compliant with HMRC?
Keep clean records, reconcile regularly, follow a VAT checklist and submit on time using MTD-compatible processes
Parul is a content specialist with expertise in accounting and bookkeeping. Her writing covers a wide range of accounting topics such as payroll, financial reporting and more. Her content is well-researched and she has a strong understanding of accounting terms and industry-specific terminologies. As a subject matter expert, she simplifies complex concepts into clear, practical insights, helping businesses with accurate tips and solutions to make informed decisions.

