The UK Budget 2025, delivered on 26 November 2025, introduces substantial changes that will reshape employer payroll costs, benefits administration, and payroll compliance.
From National Living Wage increases to pension contribution rules and employer national insurance adjustments, these measures demand immediate attention.
This comprehensive guide examines what the Budget means for businesses and how employers can prepare for the changes ahead.
Key Takeaways
- Minimum and Living Wage rise from April 2026, increasing payroll costs, especially for younger staff.
- From April 2029, pension salary sacrifice over £2,000 will face employer and employee National Insurance.
- Employer National Insurance thresholds stay frozen until 2031, pushing up payroll costs as wages grow.
- Dividend tax goes up from April 2026, affecting business owners who take income as dividends.
- Tax relief for homeworking expenses ends April 2026, but employers can still reimburse costs without tax.
- Employers should update payroll systems, plan budgets, and communicate changes clearly to staff.
National Minimum and Living Wage Increases (April 2026)
One of the most immediate impacts on employer payroll costs comes from wage increases. The government confirmed new rates taking effect from 1 April 2026.
| Category | Current Rate | New Rate (April 2026) | Percentage Increase |
|---|---|---|---|
| National Living Wage (21+) | £12.21 | £12.71 | 4.1% |
| 18-20 Year Olds | £10.00 | £10.85 | 8.5% |
| 16-17 Year Olds | £7.55 | £8.00 | 6.0% |
| Apprentice Rate | £7.55 | £8.00 | 6.0% |
| Accommodation Offset | £10.66 | £11.10 | 4.1% |
The sharper rise for 18-20-year-olds demonstrates the government’s commitment to closing the age gap. The long-term aim involves moving towards a single rate for everyone aged 18 and over. For employers, particularly in retail, hospitality, and care sectors, this means significantly higher payroll costs.
Impact on Small Businesses
Sectors with younger workforces will feel these changes more acutely. The 8.5% increase for 18-20-year-olds represents a substantial jump in labour costs.
Small businesses must review budgets now and ensure payroll systems automatically apply these new rates. Failure to implement correct rates could result in underpayment penalties and compliance issues.
Salary Sacrifice Pension Cap
Perhaps the most significant change affecting employer contributions comes from pension reforms. From 6 April 2029, pension salary sacrifice rules undergo a fundamental transformation.
How the New System Works?
Currently, salary sacrifice arrangements allow employees to exchange salary for employer pension contributions. This arrangement avoids both employer and employee National Insurance contributions entirely.
From April 2029, only the first £2,000 of pension contributions via salary sacrifice remains NIC-exempt. Contributions above this threshold will attract both employer NIC (15%) and employee NIC (8% below £50,270, then 2%).
Who This Affects?
Anyone earning above £40,000 in a salary sacrifice arrangement faces higher costs. The minimum auto-enrolment contribution level is 5% of qualifying earnings.
This measure particularly impacts higher earners using salary sacrifice for tax efficiency.
Practical Example
Consider an employee earning £120,000 who saves £20,000 into their pension via salary sacrifice. This strategy currently brings taxable income to £100,000, preserving the personal allowance.
From April 2029, this would result in:
- Employer paying an additional £2,700 in NICs
- Employee paying an additional £360 in NICs
The tax relief on income tax remains unchanged, but the NIC savings disappear above £2,000.
Planning for Employers
- Start modelling these cost now, even though implementation is four years away.
- Review enhanced pension contributions and bonus sacrifice schemes.
- Consider how this affects your total reward strategy and employee benefits packages.
- Early planning with payroll and benefits teams prevents last-minute surprises and budget shortfalls.
Major updates:
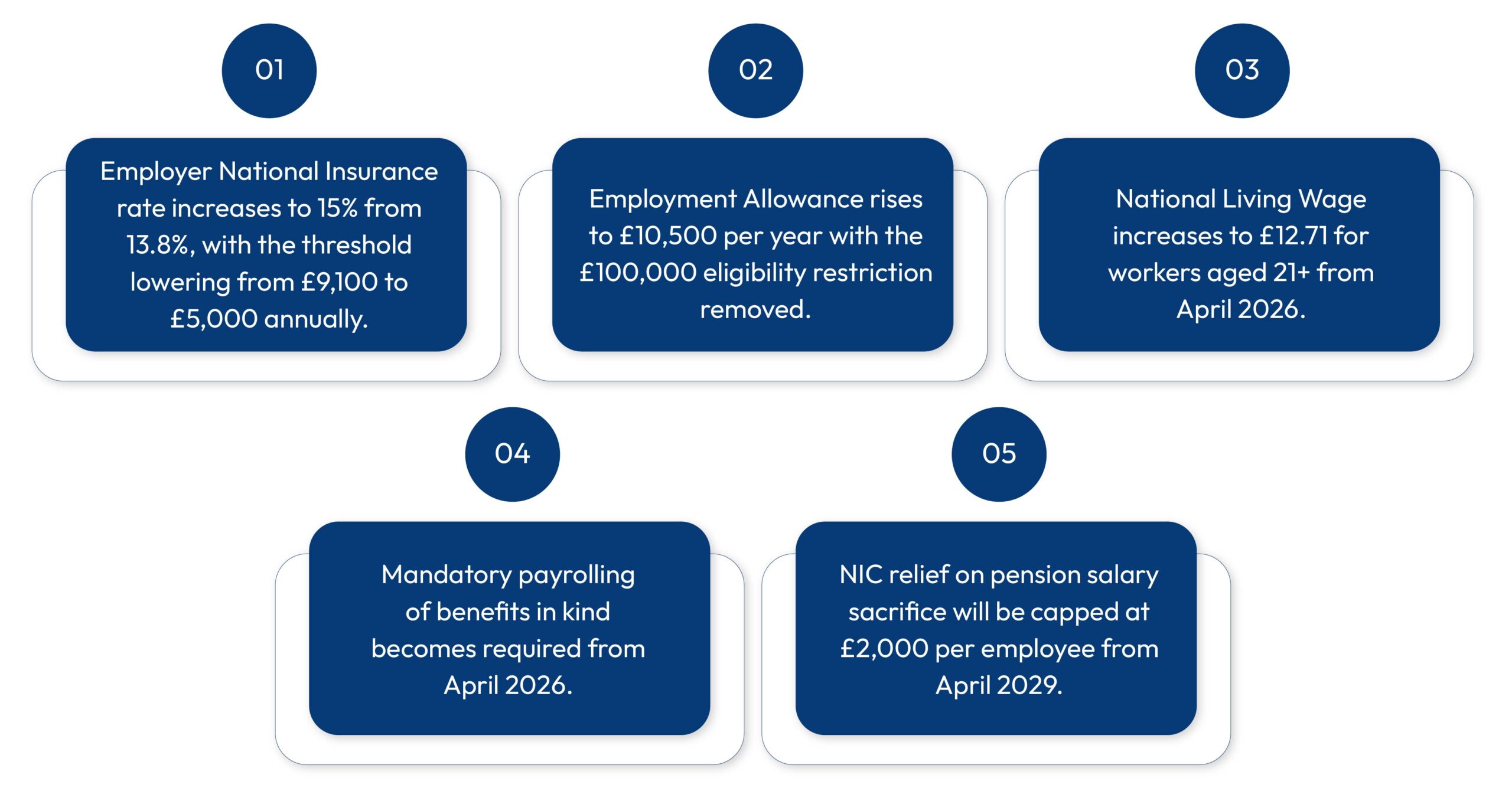
Employer National Insurance and Threshold Changes
The Budget maintains the Secondary Threshold for employer NIC at current levels until April 2031. This represents an extension of the previous freeze announced in earlier budgets.
Employment Allowance Considerations
The Employment Allowance helps smaller employers offset their National Insurance liability.
Understanding how threshold freezes interact with this allowance is crucial for payroll support for small businesses.
While the Budget doesn’t change Employment Allowance amounts directly, employer payroll costs continue rising through wage increases.
NIC Calculation Changes Over Time
With wages rising but thresholds frozen, more earnings fall subject to employer National Insurance.
This phenomenon, known as fiscal drag, gradually increases the tax burden without raising rates.
Employers should factor this into long-term financial planning and workforce cost projections.
Income Tax and Personal Allowance Freezes (Until 2031)
The Chancellor confirmed that income tax thresholds remain frozen until April 2031. This affects employees directly but has implications for employers too.
Key Thresholds Remaining Frozen
- Personal allowance: £12,570
- Higher rate threshold: £50,270
- Additional rate threshold: £125,140
What This Means for Employees?
As wages rise, more employees slip into higher tax bands without rates changing. This fiscal drag means employees feel their pay doesn’t stretch as far. Employers may face increased pressure for salary reviews or enhanced benefits packages.
Employer Responsibilities
HR and payroll teams must understand these impacts to explain them clearly to employees. Factor this into workforce planning and consider how benefits might offset reduced take-home pay.
Clear communication about tax thresholds helps manage employee expectations during salary discussions.
Dividend Tax Increases (April 2026)
From April 2026, dividend tax rates increase by 2 percentage points:
- Basic rate: 10.75% (up from 8.75%)
- Higher rate: 35.75% (up from 33.75%)
Impact on Business Owners
This directly affects owner-managers who take income via dividends. Companies structured as limited businesses need to review profit distribution strategies.
Salary payments could become relatively more attractive compared to dividends.
Strategic Review Required
Model the options now with your accountant or payroll provider. Consider how this affects director remuneration and overall tax efficiency.
The balance between salary and dividends shifts with these new rates.
Employment Rights Bill and Shift Payment Changes
New regulations require employers to compensate workers for cancelled, moved, or curtailed shifts. The Budget confirms these payments are subject to income tax.
What Employers Need to Know?
This represents a significant change for businesses with shift-based workforces. If you haven’t already, seek advice on the Employment Rights Bill’s full impact. Payroll systems must correctly tax these compensation payments from implementation.
Image Rights Payments (April 2027)
From 6 April 2027, all image rights payments related to employment face taxation as employment income. They become subject to income tax and both employer and employee National Insurance contributions.
Who This Affects?
This primarily impacts high-profile individuals like athletes and entertainers. However, any employer making image rights payments must adjust payroll processing accordingly.
Homeworking Expenses: Abolition from April 2026
The government removes the income tax deduction for non-reimbursed homeworking expenses from April 2026.
What Changes?
Employees currently claiming homeworking expenses (around £312 annually) lose this benefit. However, employers can still reimburse employees for eligible costs without deducting tax or NICs.
Strategic Considerations
Many employers see this as encouraging office returns. With rail fares frozen, there’s a clear push towards more office-based working. Consider how this affects employees managing school runs or other commitments. Employers who downsized office space during remote working may face new capacity challenges.
Expanded Workplace Benefits Relief (April 2026)
From 6 April 2026, the income tax and National Insurance exemption extends to cover:
- Eye test reimbursements
- Homeworking equipment
- Flu vaccinations
Benefits for Employees and Employers
This means lower tax and NICs on everyday work-related costs. However, the delayed implementation until April 2026 means savings don’t arrive immediately. While modest, this represents a welcome relief for both employers and employees.
Payroll Compliance: What Employers Must Do Now?
The Budget 2025 introduces multiple payroll tax changes requiring immediate attention. Effective payroll compliance demands preparation well before implementation dates.
Immediate Actions for Employers
- Review payroll systems: Ensure they can handle new wage rates automatically from April 2026
- Budget planning: Model increased employer payroll costs from wage increases and NIC changes
- Pension scheme review: Assess salary sacrifice arrangements and plan for 2029 changes
- Communication strategy: Prepare to explain threshold freezes and tax changes to employees
- Benefits audit: Review total reward packages considering dividend tax increases
Long-term Planning Considerations
Start planning for 2029 pension changes now, despite the four-year timeline. Consider how apprenticeship funding changes could benefit workforce development. Review remote working policies in light of homeworking expense abolition. Model different remuneration strategies accounting for dividend tax increases.
Frequently Asked Questions
How will Budget 2025 affect employer NIC in the UK?
The Budget maintains the Secondary Threshold for employer NIC at current levels until April 2031. However, increasing wages mean more earnings subject to employer national insurance. Combined with minimum wage increases, total employer payroll costs will rise significantly.
What businesses need to know about NIC changes in 2025?
The key NIC change involves salary sacrifice pensions from April 2029. Only the first £2,000 of pension contributions via salary sacrifice remains NIC-exempt. Thresholds remain frozen, creating fiscal drag as wages rise.
Will employer NIC rise in April 2025?
The NIC rate increase actually occurred in April 2025 following Autumn Budget 2024 announcements. Budget 2025 maintains the Secondary Threshold at current levels until 2031. The main impact comes from wage increases pushing more earnings into NIC calculations.
What is the impact of lower NIC thresholds on small businesses?
Lower thresholds combined with wage increases mean higher employer payroll costs. Small businesses pay employer NIC on more of their wage bill. The Employment Allowance helps offset some costs, but planning remains essential.
Are pension salary sacrifice contributions taxed from 2029?
Yes, from April 2029, employer and employee NIC applies to contributions above £2,000 annually. Income tax relief on pension contributions remains unchanged. This represents a significant change to the tax efficiency of salary sacrifice.
How much more will employers pay in NIC in 2025?
Actual increases depend on wage bills and employee numbers. Minimum wage increases of 4.1% to 8.5% significantly impact labour-intensive sectors. Combined with frozen thresholds, most employers face higher total NIC bills.
What is the new Employment Allowance amount for 2025-26?
The Budget 2025 doesn’t announce changes to Employment Allowance amounts. The allowance continues at current levels, offsetting some employer NIC liability. Small businesses should claim this to reduce employer national insurance costs.
What steps should SMEs take before the NIC increase in 2025?
Review budgets accounting for minimum wage increases from April 2026. Model the impact of pension salary sacrifice cap for 2029 planning. Consider whether outsourced payroll services provide better compliance support. Audit total reward packages and consider apprenticeship opportunities.
How do salary sacrifice pension cap changes affect higher earners?
Anyone contributing more than £2,000 annually via salary sacrifice pays additional NICs. For someone contributing £20,000, this could mean £3,060 extra in combined NICs from 2029. The tax efficiency of high-level salary sacrifice significantly reduces.
When do the new National Living Wage rates take effect?
New rates take effect from 1 April 2026. Payroll systems must automatically apply these rates from that date. Failure to implement correct rates results in underpayment penalties.
How does the dividend tax increase affect small business owners?
Basic rate taxpayers pay 10.75% (up 2%) and higher rate taxpayers pay 35.75% (up 2%). This makes salary relatively more tax-efficient compared to dividends. Review your remuneration strategy with professional advisors.
What are the key pension contribution rules changes in Budget 2025?
The main change caps NIC relief on salary sacrifice at £2,000 from April 2029. Income tax relief remains at current generous levels. Auto-enrolment minimum contributions continue unchanged at 5%.
How can employers prepare for payroll changes in 2026?
Start now by reviewing payroll systems and budgets. Communicate changes clearly to employees, particularly regarding tax thresholds. Consider professional payroll support if internal resources feel stretched.
What apprenticeship funding is available for SMEs from 2026?
SMEs receive 100% government funding for training costs of apprentices under 25. This significantly reduces barriers to apprenticeship programmes. Focus resources on mentoring rather than training costs.
How does the homeworking expenses abolition affect employees?
Employees lose the £312 annual deduction from April 2026. However, employers can still reimburse actual costs without tax deductions. This represents a push towards more office-based working.
Parul is a content specialist with expertise in accounting and bookkeeping. Her writing covers a wide range of accounting topics such as payroll, financial reporting and more. Her content is well-researched and she has a strong understanding of accounting terms and industry-specific terminologies. As a subject matter expert, she simplifies complex concepts into clear, practical insights, helping businesses with accurate tips and solutions to make informed decisions.

